A unique case of calcinosis in a patient with systemic sclerosis treated with spinal cord stimulation
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article or claim that may be made by its manufacturer is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
Authors
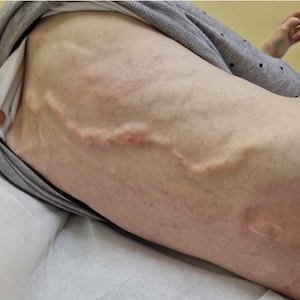
Systemic sclerosis (SSc) is a complex autoimmune disease presenting with a wide organ-manifestation. One out of three patients with SS is affected by calcinosis, i.e. the deposition of apatite in soft tissue. The association between digital ulcers and calcinosis suggests a role of tissue hypoxia and inflammation in its pathogenesis. Treatment of SSc related ulcers and calcinosis includes immunosuppressive agents, autologous haematopoietic stem cell transplantation, calcium channel blockers, phosphodiesterase 5 inhibitors iloprost or bosentan. Different reports provided promising results about the effect of spinal cord stimulation in the management of digital ulcers, in terms of pain relief and improvement in microcirculation. None of these reports describe the possibility to retrieve calcinosis around the epidural catheter or the pulse generator. The present case report describes a unique case of calcinosis distributed around the pulse generator in a patient with SSc and digital ulcers.
How to Cite

This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License.






